Why Are My Fingers Numb?
Table of Contents
- Any Numbness Means It's a Nerve Problem
- 10 Main Reasons for Finger Numbness
1) Overuse Injury
2) Peripheral neuropathy
3) Carpal tunnel syndrome
4) Cubital tunnel syndrome
5) Tendonitis
6) Raynaud's phenomenon
7) Dupuytren's contraction
8) Ganglion cysts & tumors
9) Scleroderma
10) Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
This article explores the 10 most common causes of finger numbness, starting with those doctors see most often. Finger numbness can come from many different issues, but it’s rarely random. When it’s paired with other symptoms—like tingling, burning, or pain—you can often pinpoint the exact cause. Understanding these patterns can help you recognize what’s really happening in your hands and guide you toward the right treatment or next steps.
Any Numbness Means it's a Nerve Problem
Any numbness you feel means it's a problem with your nerve. That problem is called
neuropathy. And the abnormal feelings it produces (like numbness) are known as
paresthesia.
Paresthesia is an unusual feeling you get on the skin with nothing seemingly causing it. Numbness is just one of those feelings. It could also feel like burning, pain, tingling, itching, prickling, etc.
Any of these paresthesia sensations can occur only once (“transient”) or they can be long-lasting ("chronic”). Usually, chronic finger numbness has a more serious underlying cause. Chronic numbness in the fingers can be due to any one of the following conditions - which are described in detail below:
- Overuse injury
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Cubital tunnel syndrome
- Tendonitis
- Raynaud's phenomenon
- Dupuytren's contraction
- Ganglion cysts & tumors
- Scleroderma
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
10 Main Reasons for Finger Numbness
Overuse injuries are the most common cause of finger numbness and pain. They occur by repetitively and forcefully moving your fingers or holding them in an awkward position. The result is stress on the tendons and muscles at or near a particular joint.
It’s common for numbness, pain, or tingling to radiate out from the affected area. That means if you overwork your hands by, say, using a screwdriver, then pain or numbness can be felt at the fingertips or elbow.
Typically, certain occupations are known for causing overuse injuries. That's because they require performing
harmful hand and finger activities. Those occupations include:
Treating overuse injuries is relatively simple. Rest and avoidance are the most common recommendations by doctors. Other measures like using ice or
heat,
stretching exercises, and
massage can also help.
2. Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy refers to a number of disorders where the result is damage to part of the
peripheral nervous system. Those are the nerves running through your limbs and skin.
In the fingers and hand, these nerves carry signals between the hand and the brain. The signals include, pain, temperature, vibration, fine touch, heat, etc. from the skin.
Many of the conditions listed in this article are actually different types of peripheral neuropathy. That’s why neuropathies are usually classified according to the problems they cause (e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome). Neuropathies are also classified by how extensively the nerves are damaged (i.e.,
mononeuropathy and polyneuropathy).
At its source, neuropathy means nerves are injured or damaged. Nerve damage is what causes finger numbness, pain, tingling, burning, soreness, itching – and a host of other sensations.
Neuropathies are either acquired, hereditary or of unknown origin. The most common are the
acquired neuropathies. They can have an environmental cause such as trauma, toxins, illness, or infection. The most commonly known causes of acquired neuropathies are:
Neuropathy treatments depend on the type of nerve damage, the location, and which symptoms you have. Addressing and targeting the cause often results in the neuropathy resolving by itself. Sometimes a combination of therapies is most effective. These include:
3. Carpal tunnel syndrome
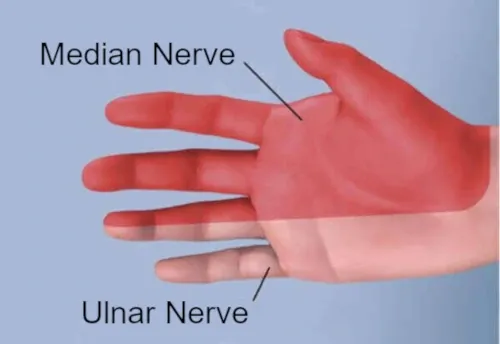
Carpal tunnel syndrome happens because of neuropathy along the
median nerve. This nerve runs from the arm to the hand. It passes through a narrow space in the wrist called the
carpal tunnel (hence the name of the disorder).
Travelling right next to the nerve,
flexor tendons also run from the arm to the hand. And that’s the problem. When these tendons swell (as from over-work or stress) they push on the median nerve and compress it. Eventually, more swelling means the nerve gets crushed.
4. Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
This disorder is similar to carpal tunnel syndrome (above). But in
cubital tunnel syndrome, the ulnar nerve (not the median nerve) has the neuropathy and subsequently causes paresthesia.
The
ulnar nerve runs from your shoulder to your hand. On its way, it passes through another narrow space at the elbow. This is called the cubital tunnel (hence the name of this disorder).
As the cubital tunnel swells, it traps and compresses the ulnar nerve. More swelling means more nerve compression. That compression is what causes finger numbness, particularly in the ring and little fingers. As with carpal tunnel syndrome, you can also feel pain, tingling, and weakness in the ring and little fingers.
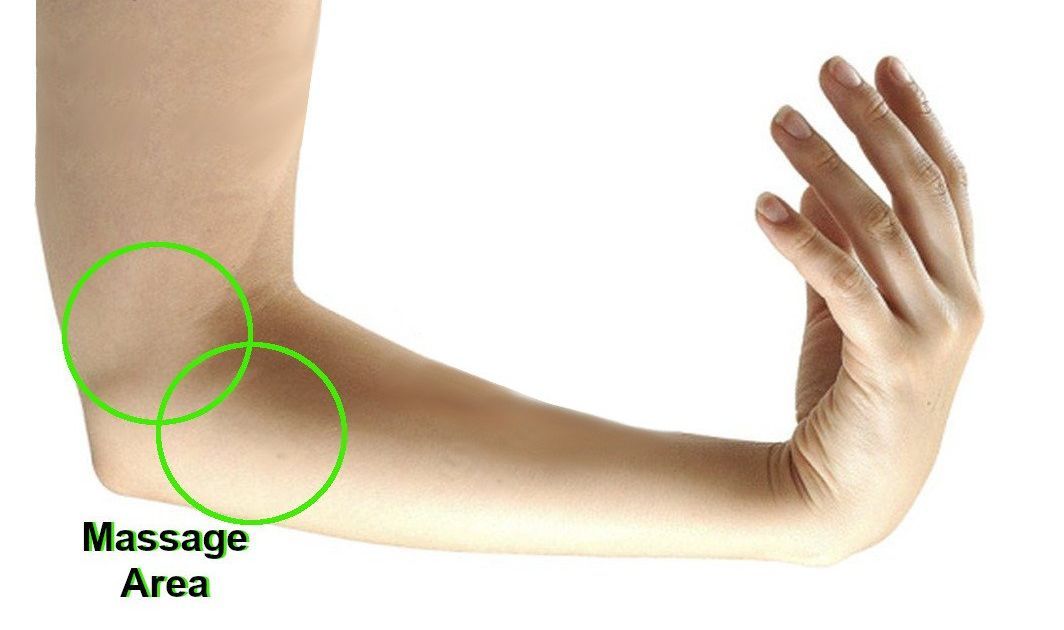
Treating cubital tunnel syndrome starts with nonsurgical remedies. Chief among them is massaging the inner elbow area as shown in the photo. However, it it’s severe, then surgery may be required to decompress the ulnar nerve.
5. Tendonitis
Tendinitis occurs when tendons inflame and swell. Usually it happens near a joint, which is why the hand and fingers are often affected.
You can get tendonitis by accident or injury, as well as simply by over-working a joint. Symptoms can occur anywhere along the tendon where there’s inflammation and swelling. This swelling is what causes finger numbness, pain, and tingling.
In fact, you can usually tell if you have tendonitis by tapping the area where you feel discomfort ("percussion test"). Pain or soreness indicates tendonitis.
The location of the tendon swelling defines the name of the tendonitis. For instance:
- Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) is tendon inflammation at the back side of the forearm and elbow joint.
- Golfer's or baseball elbow (medial epicondylitis) is what causes numbness and pain anywhere from the wrist to the elbow on the forearm’s palm side.
- Rotator cuff tendonitis
(biceps tendonitis) occurs at the shoulder. Symptoms occur due to inflammation of tendons around the shoulder capsule.
- Trigger finger
is when the covering (sheath) of a finger tendon inflames. As a result, the tendon doesn’t glide smoothly. That means you can’t flex or extend the finger. Most times you feel the finger lock up, then suddenly it releases - like a trigger.
Treating tendonitis is relatively easy. Usually simple rest and occasional massage will ease the tendon inflammation. It might take 1-2 weeks of care, but symptoms almost always resolve completely.
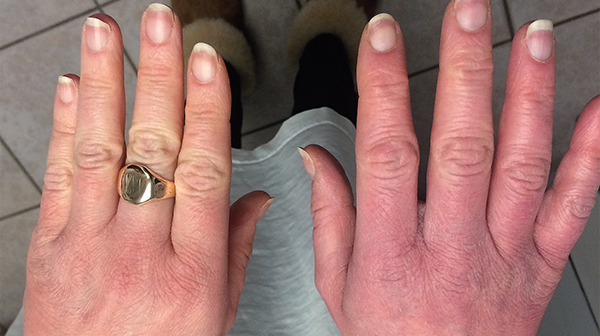
6. Raynaud's phenomenon
Raynaud's phenomenon (or disease) occurs as two distinct types: Primary and Secondary. Primary Reynaud’s is not as serious and is usually milder and more manageable. Secondary Raynaud's generally displays more severe symptoms.
A main cause of Secondary Raynaud's is exposure to
vibrating power tools (saws, jackhammers, drills, etc.). It produces
Vibration White Finger, a variant of Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS).
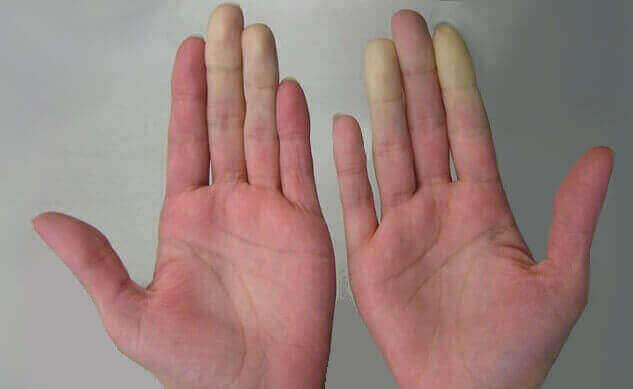
This phenomenon occurs when the small blood vessels in fingers and hands become over-sensitive to the slightest changes in cold temperatures. It results in a “Raynaud's attack”. This is a flare-up, when the fingers change color from white, to blue, to red.
There is no cure for Raynaud's phenomenon. But patients can make changes in their lifestyle to prevent flare-ups. Also, some medications can help reduce symptoms severity.
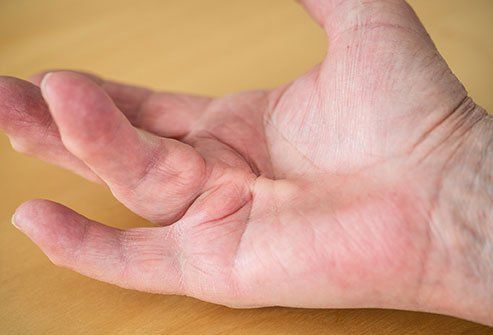
7. Dupuytren’s Contracture
Dupuytren's contracture is when the connective tissue between the tendons and skin in the palm abnormally thicken. This causes one or more fingers, when at rest, to be pulled inward toward the palm.
Usually the affected fingers are bent. Patients cannot lay their palm flat on a table. Often, there’s a palpable nodule or lump in the palm.
Dupuytren’s contracture most often causes pain. But it can also be one of the causes of finger numbness, especially in the advance stages.
During the early stages of the disorder, treatment for Dupuytren’s contracture can be as simple as doing finger stretching exercises. But when it’s more advanced,
other treatments such as injections of steroid or enzymes (Xiaflex) are needed to break up the thickened tissues. Needle aponeurotomy and surgery are reserved for the more stubborn cases.
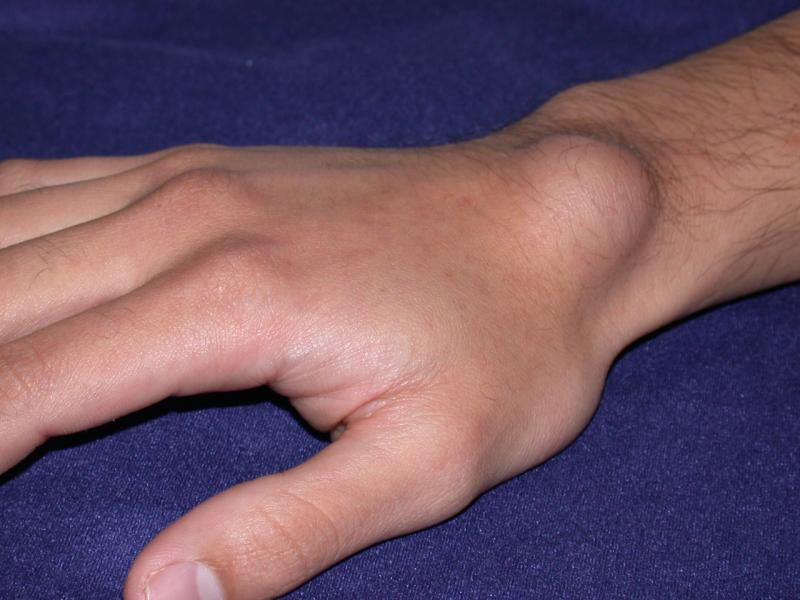
8. Ganglion cysts & tumors
A tumor is any abnormal group of cells in the body. While such cells are usually thought of as cancer, the majority of hand and finger tumors are not cancerous.
The most common tumor of the hand is a
ganglion cyst. It grows either on the inner side of the wrist or on top. They are generally filled with fluid.
However, if the cyst is near one of the major nerves of the hand (i.e., median or ulnar nerves) it could cause compression and neuropathy. As a result, it could cause finger numbness, tingling, or pain.
Usually small ganglion cysts require no treatment because they can resolve by themselves. But if the cyst is large or causing numbness, pain, or is inhibiting joint movement, other measures are needed.
Immobilizing the joint usually helps because joint movement can make the cyst bigger. If that doesn’t help, your doctor may
aspirate the cyst. That means using a needle to drain the fluid inside it. But that doesn’t guarantee the cyst won’t fill up with fluid again. The final treatment is surgery to remove the cyst.
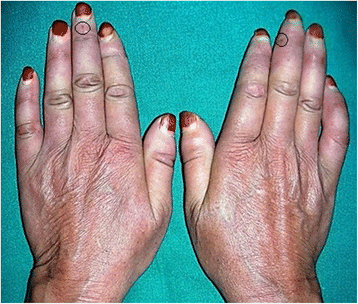
9. Scleroderma
Scleroderma represents a group of related conditions. It usually results in abnormal growth and thickening of connective tissues beneath the skin (also around your internal organs).
Scleroderma can make the skin over your fingers tight and thick. This restricts movement of the fingers and hand.
You can also have
systemic scleroderma. This causes the blood vessels of the hand and fingers to constrict. The resulting diminished blood flow in systemic scleroderma is what causes numbness, tingling, and pain.
Scleroderma has no cure. But treatments include blood pressure medicines, steroids, and immunosuppressing agents. These treatments can reduce the symptoms significantly. Moreover, these treatments can also prevent scleroderma from advancing.
10. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
Pain is the primary symptom of
complex regional pain syndrome. But it also causes finger numbness, tingling, burning, stabbing, and stinging. Often it’s a mixture of these feelings. It can be intermittent or continuous.
The exact cause of complex regional pain syndrome is unknown. But it almost always appears within 1 month after an injury at or near the affected area.
There's no cure for this disorder. But the symptoms can be managed using a combination of medicine, physical therapy, and psychological support.
Summary
Nerve damage (called neuropathy) is the root cause of abnormal sensory feelings in the skin. And it's what causes finger numbness, pain, itching, tingling, and other uncomfortable sensations, called paresthesia. The cause of the nerve damage usually defines what the condition is, like carpal tunnel syndrome or cubital tunnel syndrome.
FAQs
Can you have multiple causes of finger numbness?
Yes. However, generally there is one cause that is the most severe contributor.
Is tendonitis more common than carpal tunnel syndrome or cubital tunnel syndrome?
Yes, both conditions are far less common than tendonitis (or, more broadly, tendinopathy).
Does one particular doctor or specialist cover all of these finger numbness conditions?
No. That's because the cause of the condition can vary. Therefore, a particular specialist will be required to help you treat the disorder. Ask your general practitioner or family doctor who you can refer to.
About