Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Causes & Risk Factors
Of the many potential carpal tunnel syndrome causes, more than one may trigger this painful and numbing condition. In fact, it's the norm for a combination of factors to produce the symptoms of carpal tunnel.
However, in many instances there's no definite factor or factors to point to as the culprit. That's because in some patients, carpal tunnel syndrome seems to "just happen" for no apparent reason.
Generally speaking, if you have
carpal tunnel symptoms, you can bet one or more of the risk factors listed below puts you in the position to develop this disorder.
Carpal tunnel syndrome causes
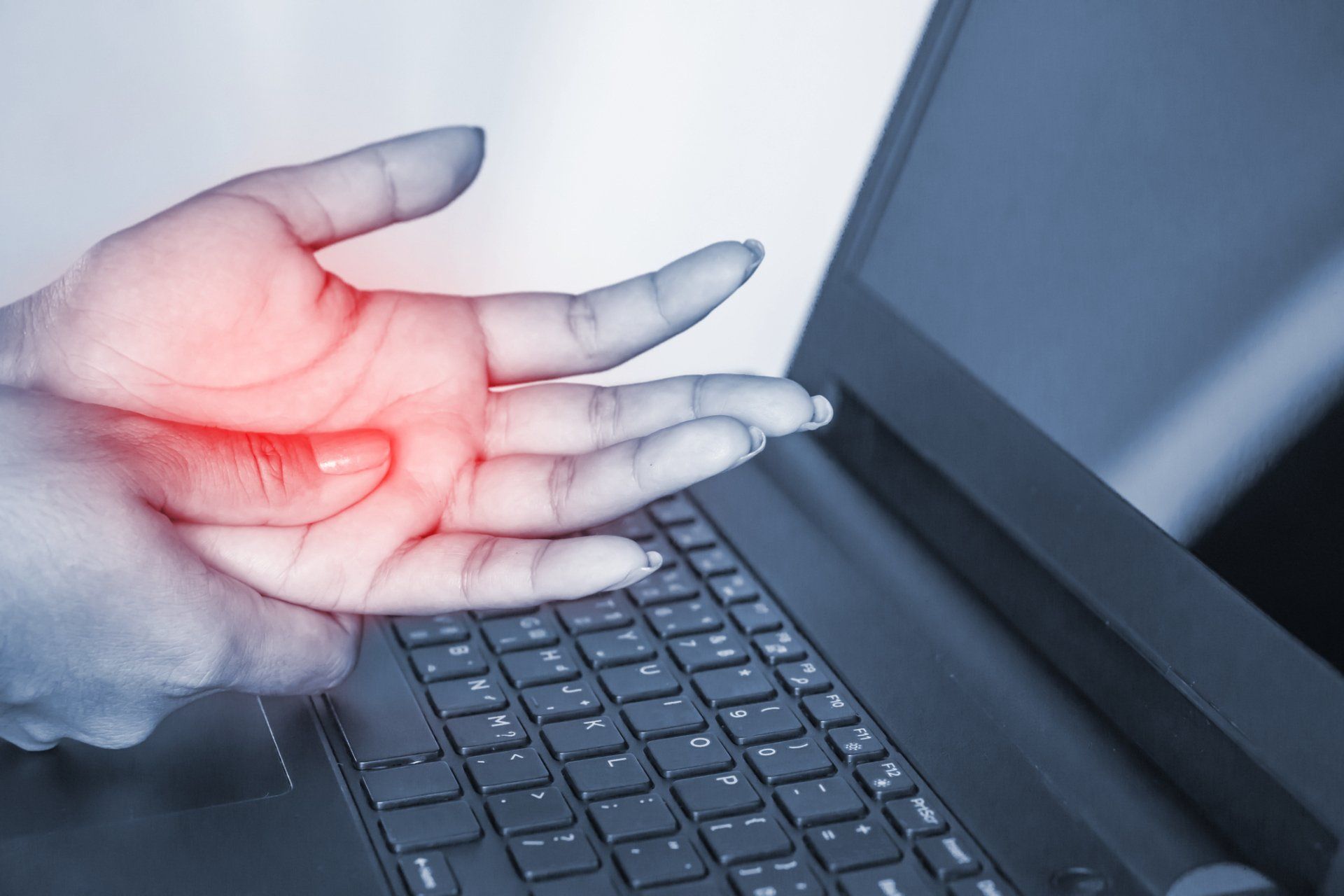
Over 4 million Americans suffer with carpal tunnel syndrome. Causes of this condition directly or indirectly point to problems deep inside the wrist joint.
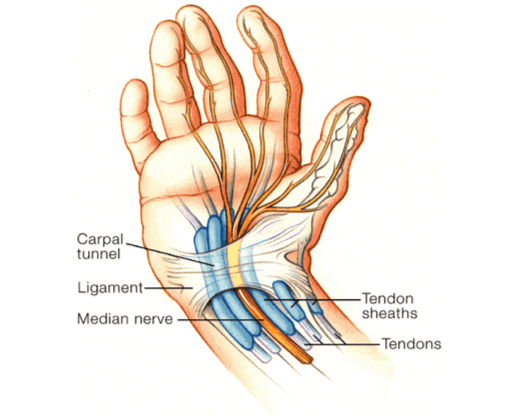
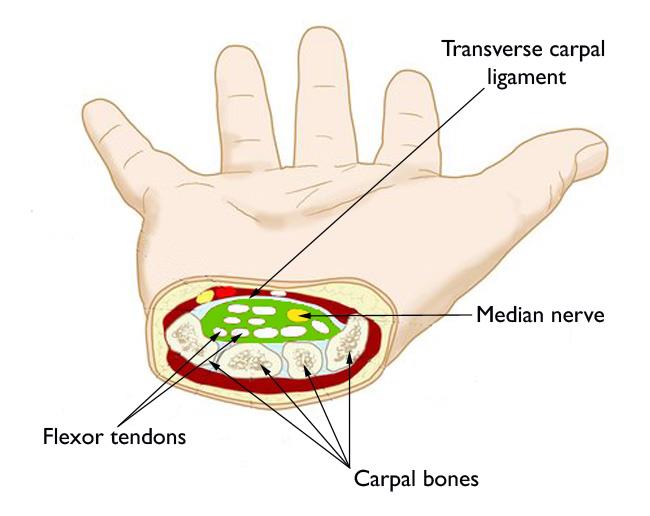
The basic problem occurs in a space or passageway inside the wrist called the
carpal tunnel. Inside this passageway, several important structures run from the hand to the arm. These are
flexor tendons (which are responsible for curling your fingers), blood vessels, and the
median nerve.
The median nerve is one of the main nerves of the hand. It's responsible for feelings (sensations) in the palm and fingers. It's also the nerve responsible for moving muscles in your fingers.
Due to one of the reasons listed below, sometimes these flexor tendons
inflame and swell with fluid pressure. But the carpal tunnel is a solid passageway with no room to expand. As a result, the pressurized tendons are forced to push against the median nerve.
Slowly, more and more pressure builds up, which starts to crush the median nerve. Nerves don't like being crushed; think of leaning on your elbow (or "funny bone"). That's the ulnar nerve being crushed, resulting in finger tingling.
Eventually the fluid pressure inside the carpal tunnel passageway becomes so great that the median nerve is completely crushed by the swollen tendons.
It's this crushing that produces all of the unusual feelings or
symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome.
What carpal tunnel syndrome feels like
We've learned the key to understanding carpal tunnel syndrome: causes of all the symptoms are due to tendon swelling.
These swollen tendons slowly crush the median nerve with intense fluid pressure.
And it's this crushing process which produces all of the unusual feelings or symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. These are:
- Numbness or tingling (also called "pins & needles") in the fingers or hand. Sometimes it's so severe that it wakes you up while trying to sleep. Your thumb, index and middle fingers are usually most affected. But the little (pinky) finger is never affected.
- Many patients report "electric shock" feelings shooting from their fingers or hand into their arm.
- Pain is a problem in about half of carpal tunnel patients. When pain occurs, it can be severe. Sometimes it can feel sharp but in an hour it might feel dull.
Pain is most often felt when the hand is at rest.
- Hand weakness and loss of grip strength usually results alongside severe numbness. Patients feel their hand or grip isn't as powerful, especially when making the pinching motion. Clumsiness is another consequence, and dropping things is common.
Carpal tunnel symptoms can be mild or intense. Oftentimes symptoms are most troublesome at night, when trying to sleep.
Severe carpal tunnel syndrome usually persists all day and night. Some patients can have one or all of the unpleasant sensations simultaneously (pain, numbness, tingling, weakness).
Causes & risk factors
Nobody is absolutely sure why a person gets carpal tunnel syndrome; causes and risk factors are often confused and conflated.
But there are certain circumstances when the PROBABILITY of getting this condition increases. This is when one or more of the following conditions are present.
The following risk factors are ranked by the highest probability first, relative to their potential for developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
1. Genetics
2. Being female
3. Pregnancy
4. Anatomy
5. Trauma
6. Repetitive stress
7. Arthritis
8. Vibration
9. Nerve damage
10. Metabolic disturbances
11. Old age
12. Obesity
13. Excessive alcohol consumption
14. Stress and anxiety
15. Liver disease
16. Hypothyroidism
17. Other medical conditions
18. Medications
19. Chronic fatigue syndrome
20. Fibromyalgia
21. Lyme disease
22. Hemodialysis
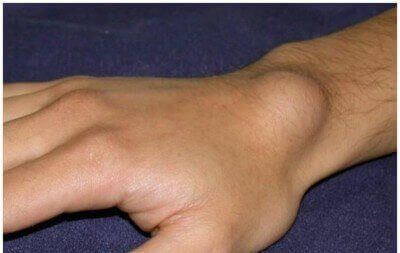
23. Tumor in the wrist
How to treat carpal tunnel syndrome
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome
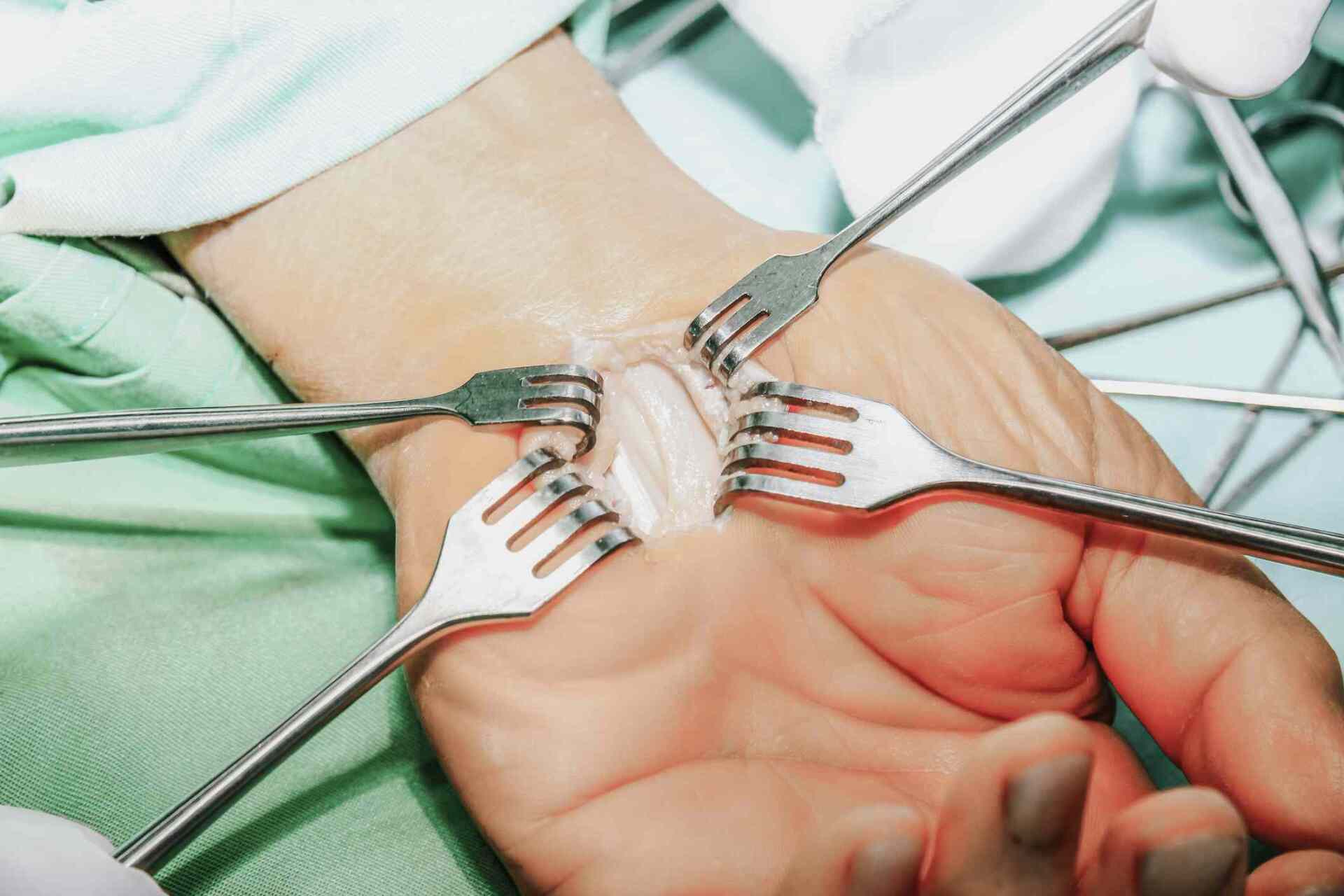
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome involves cutting the
transverse carpal ligament inside the wrist joint. Doing so allows the carpal tunnel space to snap open, thereby relieving fluid pressure accumulation.
If you're considering carpal tunnel surgery, there are numerous
pros and cons to having the operation. Taken as a whole, all surgical techniques have a modest (approximately 50%) success rate. However, they also require significant
aftercare, hand rehabilitation, and recovery times.
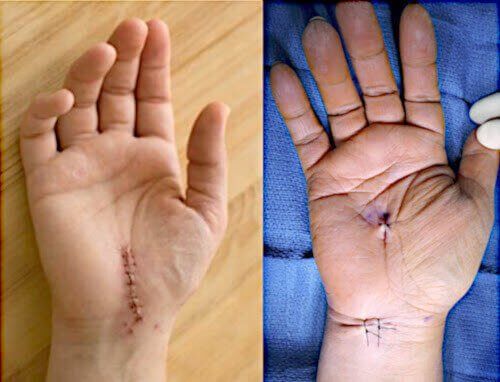
Recovery times can last 4 to 12 months, depending on complications.
There are 2 basic types of carpal tunnel surgery:
- Open carpal tunnel release surgery
- Endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery
Open carpal tunnel release surgery
With
open carpal tunnel release surgery, the surgeon makes a 2-3 inch long incision in your wrist. Then the surgeon cuts the transverse carpal ligament. Doing so allows the wrist bones to separate. Separation relieves pressure inside the carpal tunnel, and therefore, on the median nerve.
The advantage of this operation is that most surgeons have a lot of experience performing it. The long incision also gives the surgeon an unobstructed view of the wrist's interior. That means there's a lower chance of accidentally cutting a vital structure like a nerve or blood vessel.
The disadvantage of this operation is that there's more trauma and
pain due to the long incision. Also, rehabilitation and recovery takes longer than with the endoscopic technique (below).
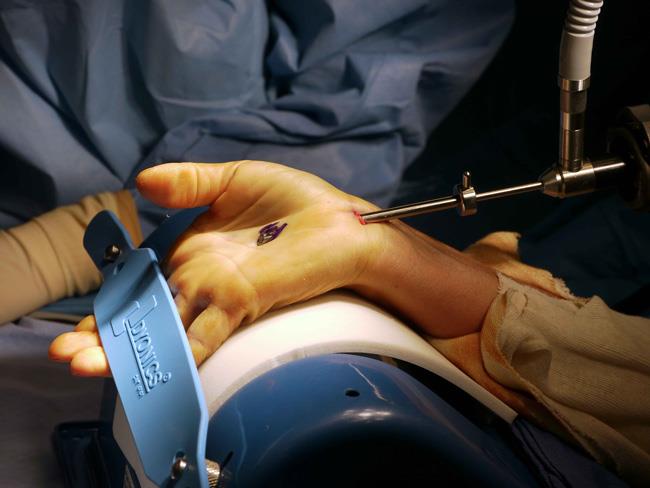
Endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery
The aim of
endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery is identical to the open release technique: to cut the transverse carpal ligament. The difference is that endoscopic surgery does not require a long incision. Instead, the surgeon makes one or two small holes in the hand. The surgeon then inserts a scalpel and camera into the hole or holes in order to see, and then cut, the ligament.
The advantage of the endoscopic technique is that there's much less hand trauma compared to the open technique. That means less hand rehabilitation and less recovery time. The disadvantage is that not many surgeons perform this operation.
Also, since the surgeon cannot see the entire field as well, there's a greater risk of accidentally cutting an important structure. This could result in, for example, nerve damage or excessive bleeding.
Non-surgical carpal tunnel treatments
The relative success of non-surgical treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome has made them the more popular therapies compared to surgery. The majority of carpal tunnel patients self-treat, and most do so successfully.
For
mild
carpal tunnel symptoms, one or two of the following remedies is usually successful. But if symptoms are
more advanced or severe,
then a combination of these remedies is required. These non-surgical carpal tunnel treatments are:
- Simple rest
- Stretching exercises
- Steroid shots
- Nocturnal bracing
- Myofascial release massage
Simple rest
As the title implies, resting an overworked hand can eliminate carpal tunnel syndrome if the symptoms have not advanced too far. That means not performing the activity that caused the problem to begin with (like typing, sewing, etc.). Mild symptoms can usually resolve in a few weeks if the activity is completely terminated. More moderate symptoms require additional therapy or therapies.
Stretching exercises
Many patients are completely misinformed about stretching exercises for carpal tunnel syndrome. They believe they must devote hours to it. Quite the contrary! Performing a
30 second stretch routine every 1-2 hours is
optimal. Doing so not only completely eliminates mild symptoms, but also prevents them from happening if you work a high risk job.
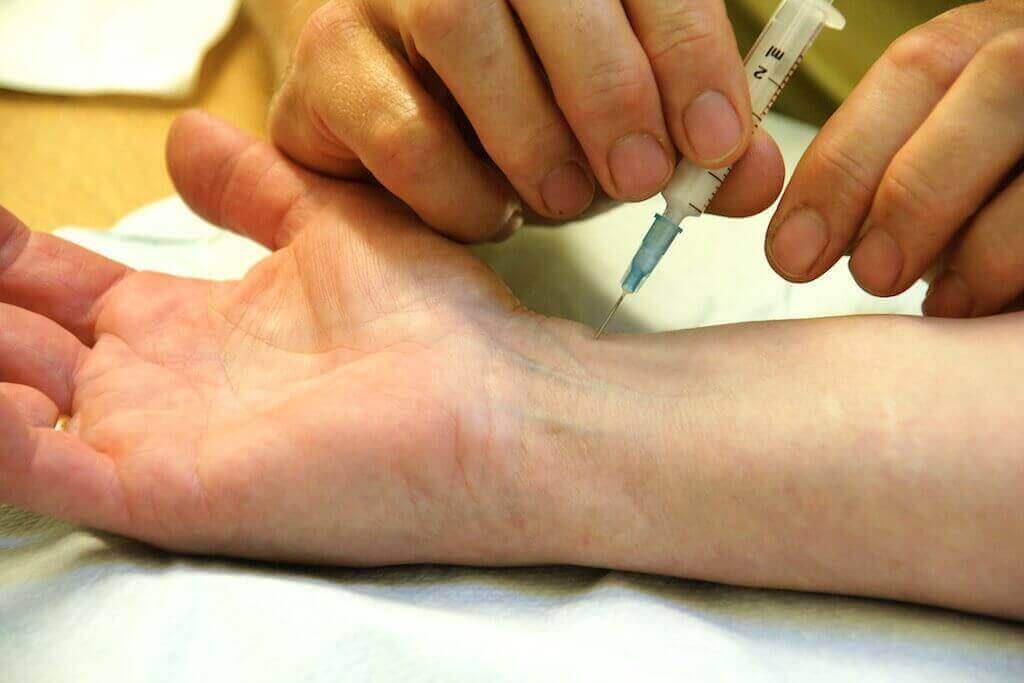
Steroid shots
Injections of corticosteroids into the wrist to relieve carpal tunnel symptoms are effective in about
45% of patients. But steroid shots are not totally safe. There are particular
side effects and potential complications. They are especially amplified if the patient has a comorbidity (such as diabetes).
Nocturnal bracing
Nocturnal bracing (night bracing) is an often-overlooked, yet powerful carpal tunnel fighter. Everyone bends their hand backward while sleeping. This increases pressure inside the carpal tunnel. That further compresses the median nerve. This is why carpal tunnel symptoms are often worse in the morning. But a night brace prevents that.
However, a
certified carpal tunnel night brace will help tremendously. That's because it will
not
have a
palmar spine. Most braces have a palmar spine, which makes the condition far worse.
And never wear a wrist brace during the daytime as you work with your hands!
You just end up fighting the brace subconsciously while working, further stressing your hand.
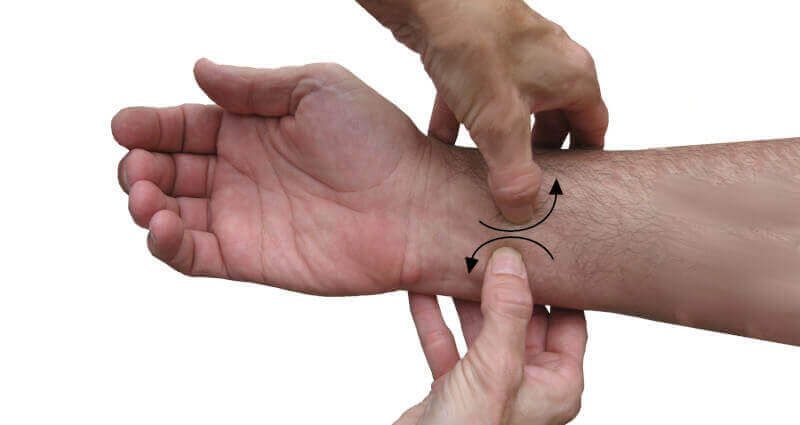
Myofascial release massage
Myofascial release massage is probably the most powerful carpal tunnel fighter. The kneading action (produced by 2 counter-rotating thumbs) breaks up adhesions and restrictions on tendons. With adhesions gone, there's no more irritation and swelling. Best of all, myofascial release massage is effective in even severe cases of carpal tunnel syndrome. But this techniques must be performed twice daily for at least 30 days to completely eliminate symptoms.
Conclusion
Of all the carpal tunnel syndrome causes, the most common are your genetics, being female, being pregnant, and performing repetitive hand activities. You should treat this disorder using nonsurgical therapies first. If they fail, then you can talk with your doctor about surgical options.